Muscle injuries, often perceived as a mere discomfort, can significantly impact daily activities and overall health. Understanding the signs and symptoms of a pulled or strained muscle is crucial for effective management and prompt recovery. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of muscle injuries, highlighting the importance of recognizing these conditions early. Through an exploration of various symptoms and preventive measures, this article aims to equip readers with essential knowledge for identifying and addressing muscle pulls and strains, ultimately fostering a more informed approach to personal health and injury prevention.
Contents
Understanding Muscle Injuries

Muscle injuries, commonly called pulls or strains, occur when fibers within the muscle are overstretched or torn. These injuries are often the result of sudden, forceful movements or overuse during physical activities. Understanding the difference between a muscle pull and strain is essential. A muscle pull typically refers to a minor tear, while a strain is a more severe injury involving significant damage to the muscle fibers. Both conditions, however, share similar causes, such as lack of proper warm-up, fatigue, overexertion, or improper technique during physical activity.
The human body comprises various muscle types, each susceptible to injury depending on the activities undertaken. Fast-twitch muscles, for instance, are more prone to injuries during explosive movements like sprinting or jumping. Slow-twitch muscles, on the other hand, may sustain injuries during prolonged, repetitive activities. Recognizing the specific activities that lead to these injuries is key to understanding and preventing muscle pulls and strains.
Initial Signs of a Pulled or Strained Muscle
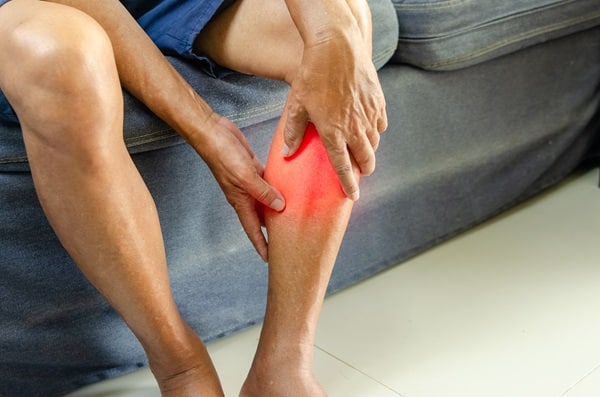
One of the primary indicators of a pulled or strained muscle is sudden, sharp pain. This pain often manifests during physical activity, signaling that the muscle has been overstretched or torn. It’s crucial to pay attention to the type of pain experienced. A sharp, intense pain usually indicates a severe muscle strain, whereas a dull, aching sensation might suggest a mild pull. The location of the pain also provides insights into the affected muscle and the severity of the injury.
In addition to pain, individuals might experience a snapping or popping sensation at the injury’s onset. This sensation, often accompanied by immediate pain, indicates that the muscle fibers have been abruptly overstretched. Following this, the affected area may become tender to the touch, further confirming the presence of a muscle injury. Immediate cessation of the activity and careful assessment of the injury are recommended to prevent further damage.
Physical Indicators of a Muscle Injury

Physical symptoms such as swelling and inflammation typically emerge following a muscle injury. These symptoms occur as the body responds to injury, aiding healing. Swelling can restrict movement and cause discomfort, signaling the need for rest and recovery. Similarly, inflammation, while a protective mechanism, can exacerbate pain and should be carefully managed.
Bruising or discoloration is another telltale sign of a muscle strain. This occurs due to ruptured blood vessels beneath the skin, resulting from tearing muscle fibers. The extent of bruising often correlates with the injury’s severity. In addition to bruising, a noticeable decrease in muscle strength or an inability to use the muscle fully can indicate a significant strain. Such symptoms necessitate a cautious approach to recovery, often involving medical consultation.
Long-Term Symptoms to Be Aware Of

Long-term symptoms can complicate recovery if a muscle injury is not adequately addressed. Persistent pain, lasting beyond the initial injury period, is a common long-term symptom. This ongoing discomfort may indicate inadequate healing or a more severe injury than initially diagnosed. Paying attention to the duration and nature of pain is crucial for assessing recovery progress.
Another long-term symptom is muscle weakness, which may persist even after the pain subsides. Weakness in the injured muscle can be a sign of incomplete healing or potential complications. It’s important to gradually rebuild strength through targeted exercises, avoiding premature or excessive strain on the recovering muscle. Chronic inflammation, characterized by prolonged swelling and tenderness, can also occur if the injury is not properly managed. Seeking medical advice for persistent or worsening symptoms is essential to ensure a safe and effective recovery.
Identifying the Severity of Your Injury

Determining the severity of a muscle injury is crucial for appropriate management. Injuries are generally classified into mild, moderate, and severe. Mild injuries, often involving minimal fiber damage, are characterized by slight discomfort and minimal impact on mobility. Moderate injuries, with more extensive fiber damage, result in increased pain and noticeable limitations in movement. Severe injuries involving complete muscle tears present intense pain, significant swelling, and substantial loss of function.
Knowing when to seek medical attention is pivotal. Mild injuries may be self-managed with proper care, but moderate to severe injuries often require professional medical assessment. Warning signs that warrant immediate medical attention include intense pain, visible deformities in the muscle, loss of sensation, or inability to bear weight on the affected limb. Timely intervention can prevent complications and aid in a more effective recovery.
Home Remedies and Immediate Care
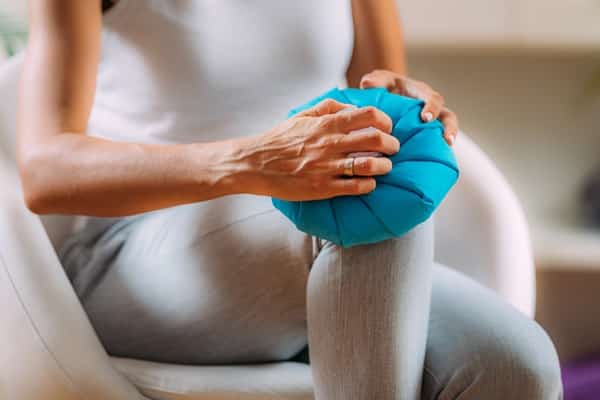

Immediate care for a pulled or strained muscle reduces pain and swelling. The R.I.C.E. method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is a widely recommended approach. Resting the injured muscle prevents further strain, while ice application reduces swelling and numbs pain. Compression with an elastic bandage provides support and limits swelling, and elevation helps reduce fluid buildup in the injured area.
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation. However, using these medications as directed and considering potential interactions with other medications is important. Additionally, gentle stretching and massage can aid in recovery, but it’s crucial to avoid aggressive movements that could exacerbate the injury. Consulting a healthcare professional before beginning any self-treatment is always advisable.
Preventing Future Muscle Injuries

Preventing muscle injuries is key to maintaining long-term health and mobility. Incorporating a thorough warm-up routine before engaging in physical activities significantly reduces the risk of muscle injuries. Warm-ups increase muscle blood flow, enhancing flexibility and preparedness for physical exertion. Similarly, post-activity, cool-down exercises help gradually reduce heart rate and muscle temperature, preventing stiffness and soreness.
Strengthening and conditioning exercises tailored to individual fitness levels can bolster muscle resilience. Regular physical activity, balanced with adequate rest periods, ensures muscles remain strong and flexible. Additionally, paying attention to proper techniques and body mechanics during exercises and daily activities can prevent undue muscle strain. A balanced diet of nutrients and hydration is crucial for muscle health and injury prevention.
The Bottom Line
Recognizing and appropriately responding to the signs of a pulled or strained muscle is critical to maintaining physical health. This comprehensive guide underscores the importance of early detection, proper immediate care, and the value of preventive measures. Individuals can effectively manage muscle health by understanding the severity of injuries, implementing effective home remedies, and taking proactive steps to prevent future injuries. Embracing a holistic approach that includes professional guidance and understanding one’s body signals further ensures a successful recovery and a resilient return to daily activities. The journey to recovery is about healing a single injury and fostering a lifelong commitment to muscle health and overall well-being.