The muscular system, a complex network in the human body, plays a crucial role in various essential functions ranging from movement to vital bodily processes. Understanding these functions is key to appreciating how muscles contribute to overall health and well-being. This blog post delves into the myriad roles of the muscular system, elucidating how it not only enables physical actions but also supports various internal mechanisms critical for survival and efficiency.
Contents
Movement And Mobility

Muscles work in concert to facilitate movement, a fundamental aspect of daily life. They operate in pairs; as one muscle contracts, its counterpart relaxes, allowing for fluid motion. This mechanism is evident in activities such as walking, where the contraction and relaxation of leg muscles propel the body forward. Moreover, fine motor skills, such as typing or playing a musical instrument, underscore the precision and coordination of muscular movements.
Posture and stability are largely maintained by the muscular system. Muscles, particularly those in the back and abdomen, constantly work to hold the body upright against gravity. This continuous activity is vital for maintaining a healthy posture, which in turn reduces the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. The subtle yet constant engagement of these muscles also illustrates the muscular system’s role in providing a stable base for movement and daily activities.
Circulation And Heart Function
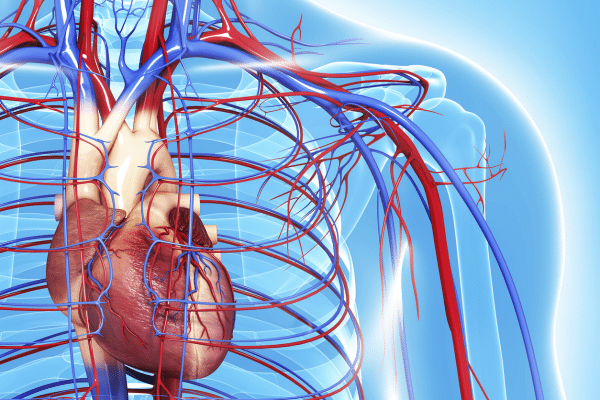
Cardiac muscles, specialized and structured for endurance and consistency, are central to heart function. Their rhythmic contractions generate the force necessary to circulate blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs. This unceasing activity of the heart muscle exemplifies its vital role in maintaining life-sustaining circulation.
In addition to the heart, skeletal muscles also contribute to circulatory health. When these muscles contract, they squeeze nearby veins, helping push blood back towards the heart. This mechanism, often referred to as the ‘muscle pump,’ is particularly important in preventing blood pooling, especially in the lower extremities. Activities such as walking or flexing leg muscles can thus be seen as vital exercises in supporting venous return and overall circulatory efficiency.
Communication And Expression

Facial muscles are fundamental in non-verbal communication and emotional expression. These muscles, when contracting in various combinations, can convey a wide range of emotions, from happiness to anger. This ability to express emotions through facial expressions is a key aspect of human communication, fostering social interactions and empathy. Additionally, muscles involved in the vocal apparatus, including those in the larynx and mouth, facilitate speech, allowing for the articulation of thoughts and feelings.
The loss or impairment of muscular function in the face can significantly impact communication abilities. Conditions such as Bell’s palsy, which causes temporary weakness or paralysis of facial muscles, can affect a person’s ability to express emotions and speak clearly. This highlights the importance of muscular health in maintaining effective communication and expression, essential components of human interaction.
Support And Structure

Muscles play a pivotal role in the structural integrity of the body. They attach to bones, providing the necessary support for skeletal structure. This connection allows for efficient load-bearing and agility, enabling the body to perform complex movements while maintaining its form. The differentiation in muscle types – skeletal, smooth, and cardiac – highlights the specialized roles each plays in supporting the body’s framework and internal organs.
Each muscle type uniquely contributes to the body’s structure and function. Skeletal muscles, attached to bones, are integral in voluntary movements. In contrast, smooth muscles, found in the walls of internal organs, are crucial for involuntary processes such as moving food through the digestive tract. Cardiac muscles, exclusive to the heart, tirelessly work to pump blood throughout the body. This diversity underlines the muscular system’s comprehensive role in body support and structure.
Breathing And Respiratory Assistance

The respiratory system’s functionality heavily relies on muscular involvement. The diaphragm, a large muscle located below the lungs, plays a pivotal role in breathing. When the diaphragm contracts, it creates more space in the chest cavity, allowing the lungs to expand and fill with air. Intercostal muscles between the ribs also assist in this process, helping to elevate the rib cage during inhalation and compress it during exhalation. This coordinated effort between the diaphragm and intercostal muscles is essential for effective breathing.
Muscular disorders can significantly impact respiratory function. Diseases affecting muscle strength and control, such as muscular dystrophy, can weaken respiratory muscles, making breathing laborious. This can lead to a reduced ability to cough and clear airways, increasing the risk of respiratory infections. The importance of muscular health in maintaining efficient respiratory function is thus underscored, highlighting the interconnectedness of different bodily systems.
Digestion And Organ Function

Smooth muscles, found within the walls of internal organs, play a critical role in the digestive process. These muscles engage in a coordinated series of contractions, known as peristalsis, which moves food along the digestive tract. This movement is essential for the mechanical breakdown of food, as well as its absorption and eventual excretion. The smooth muscles of other organs, such as the bladder, also function similarly, facilitating the storage and release of urine.
Beyond digestion, muscular activity is integral to the functioning of various organ systems. For example, the smooth muscles in blood vessels control the flow and distribution of blood, adjusting to changes in bodily demand. This adaptability ensures that organs receive an adequate blood supply under different conditions, from resting states to intense physical activity. This versatility of smooth muscles across various organ systems highlights their crucial role in maintaining bodily homeostasis.
Temperature Regulation
Muscles contribute to the regulation of body temperature through a process called thermogenesis. When the body is exposed to cold temperatures, muscles generate heat by increasing their metabolic activity. This is most apparent during shivering, where rapid, involuntary muscle contractions produce heat to maintain the body’s core temperature. This heat production is vital in cold environments, helping to prevent hypothermia.
Shivering is just one aspect of the muscular system’s role in temperature regulation. Even during non-strenuous activities, muscles continuously produce a baseline level of heat as a byproduct of their metabolic processes. This heat contributes to maintaining the body’s normal temperature, ensuring that vital enzymatic reactions occur optimally. The muscular system, therefore, plays a subtle yet constant role in keeping the body’s temperature within a narrow, healthy range.
The Bottom Line
Muscles, often associated primarily with movement, in fact, contribute to a myriad of vital functions in the human body. From supporting structural integrity and assisting in circulation to playing key roles in digestion, temperature regulation, and communication, the muscular system is integral to overall health. Understanding and maintaining this system is crucial, not just for physical strength and mobility, but for the efficient functioning of virtually all bodily processes. By highlighting the diverse and essential roles of muscles, this blog post aims to increase awareness of the importance of muscular health and encourage proactive measures to maintain it.


