Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions that can affect various muscle groups, often causing significant discomfort. While they are generally harmless, certain signs and symptoms associated with cramps warrant closer attention. This article delves into the crucial indicators that suggest a muscle cramp might be more than a temporary nuisance. From understanding their basic nature to recognizing alarming signs, it aims to equip readers with the knowledge to identify when a simple cramp could be hinting at a deeper health issue, urging timely medical consultation.
Contents
Fundamentals of Muscle Cramps
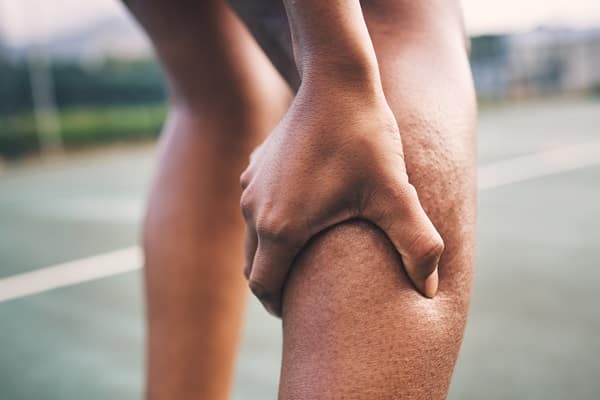

Muscle cramps are characterized by abrupt, involuntary muscle contractions that can range from mildly annoying to intensely painful. They occur when a muscle involuntarily and forcibly contracts and cannot relax. These cramps can affect any muscle but are most common in the legs. While the exact cause is often unknown, they may be related to muscle fatigue, dehydration, or mineral deficiencies. Understanding these basics is crucial for identifying when a cramp is just a temporary discomfort or a symptom of a larger issue.
The difference between common muscle cramps and those signaling potential health concerns lies in their duration, intensity, and associated symptoms. Everyday muscle cramps usually resolve quickly and are often caused by factors like overuse or dehydration. However, cramps that persist recur frequently or are exceptionally painful might indicate underlying medical conditions. Recognizing these differences is the first step in determining when to seek medical advice.
Frequency and Duration

A key factor in assessing the seriousness of muscle cramps is their frequency. Occasional cramps are common and typically not a cause for concern. However, if cramps become a frequent occurrence, interrupting daily activities or sleep, it may signal a deeper health issue. It’s important to monitor how often these involuntary contractions occur to understand their impact on overall well-being.
Regarding duration, most muscle cramps are short-lived, lasting from a few seconds to several minutes. Cramps that persist for extended periods, however, are unusual and potentially worrisome. If a muscle cramp lasts for more than a few minutes without relief, or if there are recurring episodes of prolonged cramping, this could be indicative of more serious health problems, warranting a consultation with a healthcare professional.
Intensity and Pain

The intensity of a muscle cramp can vary greatly, and understanding this variation is vital. A mild cramp may cause discomfort but typically doesn’t interfere significantly with activities. On the other hand, if cramps are so severe that they cause excruciating pain or limit mobility, this could be a sign of a more serious condition. The threshold of pain that warrants concern is when the intensity of the cramp disrupts daily life or causes unbearable discomfort.
Additionally, the nature of the pain experienced during a cramp can offer clues about its seriousness. A sharp, stabbing pain or a sensation that feels unusually different from common cramps should not be ignored. Persistent or extreme pain, especially when accompanied by swelling or skin changes, requires immediate medical attention, as it could indicate severe underlying conditions.
Location of Cramps

Muscle cramps can occur in any muscle group, but their location can sometimes be a clue to underlying health issues. Commonly, cramps occur in the calf muscles, feet, and thighs. However, cramps in unusual locations such as the abdomen, arms, or the neck might indicate specific health concerns. It’s important to note where the cramps are occurring and if the location changes over time.
Cramps in the calf muscles, for instance, are often harmless and related to overuse or dehydration. In contrast, cramps in the hands or neck might be associated with activities like prolonged writing or poor posture. However, persistent cramping in atypical areas, especially if not linked to any obvious cause, should be evaluated by a healthcare provider, as they could be symptoms of neurological or circulatory problems.
Accompanying Symptoms
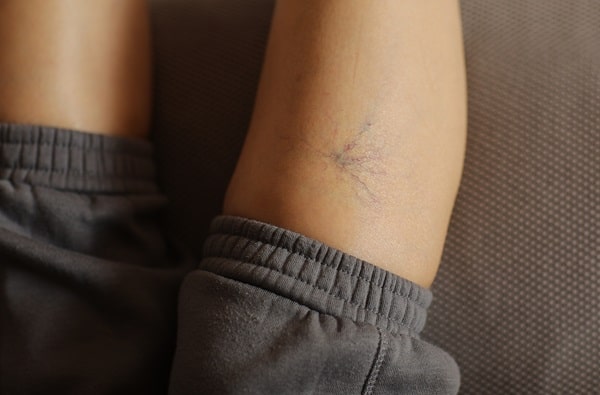
When muscle cramps are accompanied by other symptoms, it can also be an indication of a more serious health issue. Symptoms such as numbness, swelling, redness, or skin changes accompanying a cramp are particularly concerning. These additional symptoms can suggest conditions like nerve compression, blood flow issues, or infections, which require prompt medical attention. It’s crucial to observe not just the cramp but also any other unusual signs that occur simultaneously.
Another aspect to be mindful of is the presence of systemic symptoms like fever, dizziness, or severe fatigue alongside muscle cramps. This combination can be indicative of systemic illnesses, infections, or electrolyte imbalances. If these symptoms are observed, it’s important to seek medical advice, as they could signify a more complex medical condition that extends beyond the muscular system.
Risk Factors and Vulnerable Groups

Certain individuals are more prone to experiencing serious muscle cramps due to specific risk factors. People with a history of nerve disorders, circulatory problems, or chronic illnesses like diabetes and thyroid disorders are at higher risk. Additionally, older adults and athletes, due to their increased susceptibility to dehydration and muscle overuse, respectively, also fall into higher risk categories. Understanding these risk factors is essential for identifying individuals who should be more vigilant about muscle cramps.
Lifestyle factors such as poor nutrition, dehydration, and certain medications can also increase the likelihood of serious muscle cramps. Individuals who have diets low in minerals like potassium, calcium, and magnesium or those who take medications that affect electrolyte balance should be particularly cautious. Recognizing these risk factors can help in preventing cramps and identifying when they may be symptomatic of larger health concerns.
Medical History and Diagnosis

A thorough medical history is crucial in diagnosing the cause of serious muscle cramps. Healthcare professionals often look into past medical conditions, medication usage, and family history of muscle or nerve-related disorders. This information can provide valuable insights into whether the cramps are a symptom of a systemic issue or a localized muscular problem. Patients should be prepared to discuss their complete medical history for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic methods for muscle cramps may include blood tests, imaging studies, and nerve function tests. Blood tests can reveal electrolyte imbalances or metabolic issues, while imaging studies like MRI or ultrasound can assess the muscle and surrounding structures. Nerve conduction studies may be conducted if a neurological cause is suspected. These diagnostic tools are essential in pinpointing the exact cause of the cramps and formulating an effective treatment plan.
Prevention and Management

Preventing serious muscle cramps often involves lifestyle modifications. Staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet rich in minerals, and engaging in regular, moderate exercise can significantly reduce the risk of cramps. For individuals in high-risk groups, these preventative measures are even more crucial. Additionally, avoiding or moderating activities that have previously triggered cramps can be beneficial.
For managing recurring or serious muscle cramps, medical interventions may be necessary. This can include physical therapy, medication for underlying conditions, or supplements for mineral deficiencies. It’s also important for individuals to learn proper stretching and relaxation techniques, especially if their cramps are associated with physical activity. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals ensure that any changes in the cramps’ pattern or intensity are monitored, allowing for timely adjustments in management strategies.
Take Charge of Your Muscle Health
While most muscle cramps are harmless and transient, certain signs should prompt concern and a visit to the healthcare provider. Pay attention to cramp frequency, intensity, location, and accompanying symptoms. Especially for those with risk factors, proactivity in managing and preventing serious cramps is key. Remember, understanding your body’s signals and acting upon them not only addresses immediate discomfort but also safeguards long-term health. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice when cramps seem unusual or persistent.


