Canned food, a staple in households worldwide, offers a convenient and often affordable alternative to fresh produce. Its history stretches back centuries, revolutionizing how we store and consume food. However, the question remains: does this convenience come at a cost to our health? This article delves into the history, nutritional content, health benefits, and potential risks of canned foods. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview, helping readers make informed decisions about incorporating canned foods into their diets.
Contents
The History of Canned Foods

Canning as a method of food preservation has a rich history, dating back to the 18th century. It was initially developed to supply soldiers and sailors with food that wouldn’t spoil over long voyages or during wartime. This innovation drastically changed how people accessed and consumed food, making it possible to enjoy a variety of foods regardless of seasonal limitations or geographic constraints.
The evolution of canning technology over the centuries has been significant. Early methods were rudimentary and not always safe, but advancements in science and manufacturing have vastly improved the safety and quality of canned foods. Today, canning is a highly regulated and sophisticated process, ensuring that food retains its nutritional value while being safe for consumption.
Nutritional Content in Canned Foods
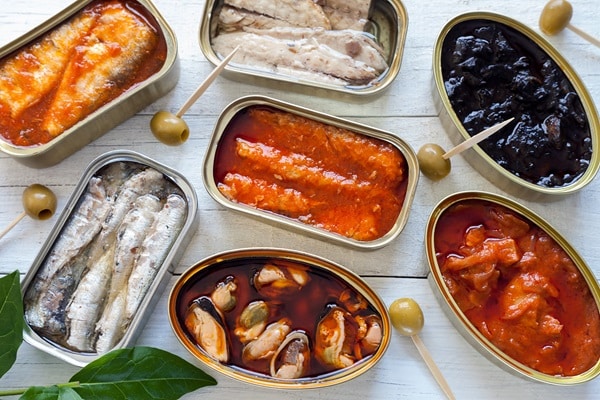

When it comes to nutrition, canned foods often face skepticism. A common belief is that they are less nutritious than their fresh counterparts. However, this isn’t always the case. Canning preserves many nutrients, especially heat-stable, such as protein and carbohydrates. Some canned foods, like tomatoes, may offer increased levels of certain nutrients, like lycopene.
On the flip side, some vitamins, particularly water-soluble ones like vitamin C and some B vitamins, can degrade during the canning process. The key is understanding that while canned foods can play a role in a balanced diet, they should complement, rather than replace, fresh produce. The nutrient profile of canned food varies, so it’s important to read labels and make informed choices.
Health Benefits of Canned Foods

Canned foods offer several health benefits, primarily due to their convenience and shelf life. They make consuming various fruits, vegetables, and proteins possible, even when fresh options are out of season or unavailable. This can significantly contribute to a balanced and varied diet, which is crucial for overall health.
Furthermore, canned foods are often a godsend in emergencies where fresh food is not an option. In these scenarios, the long shelf life and easy storage of canned foods can provide essential nutrients, making them a key component of emergency preparedness kits. However, balancing these benefits with mindful consumption is important, considering factors like sodium and sugar content in certain canned products.
Potential Health Risks

Consumers should be aware of the health risks associated with canned foods despite their benefits. One of the most discussed concerns is the presence of Bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical used in the lining of some cans. BPA can leach into food and has been linked to various health problems, though more research is needed. Many manufacturers are now producing BPA-free cans, responding to consumer health concerns.
Another risk factor is the high sodium content in many canned foods. Excessive sodium intake is a well-known health risk, potentially leading to hypertension and other cardiovascular issues. Consumers must read labels and choose low-sodium options or rinse canned foods to reduce sodium content. By being informed and selective, consumers can mitigate these risks and enjoy the benefits of canned foods safely.
Canned Food and Environmental Impact

The environmental aspect of canned foods is a topic worth exploring. The production and disposal of cans have implications for sustainability. On one hand, metal cans are among the most recyclable packaging materials available, which helps reduce their environmental footprint. The recycling process for cans requires significantly less energy than producing new cans, contributing positively to environmental conservation efforts.
However, the production process, including mining and refining the metals used in cans, can have a substantial environmental impact. Additionally, the transportation of canned goods, often heavier than fresh produce, contributes to a larger carbon footprint. Consumers must weigh these factors and support brands prioritizing sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste.
Innovations in Canning Technology

Recent advancements in canning technology have been pivotal in addressing quality and safety concerns. Innovations such as BPA-free linings, improved sealing methods, and better sterilization techniques have enhanced the overall quality of canned foods. These technological advancements ensure that food remains safe and nutritious from the production line to the consumer’s table.
Looking to the future, ongoing research and development in canning technology promise further improvements. These include reducing the environmental impact of canning, enhancing nutrient retention, and even incorporating smart packaging indicating food freshness or spoilage. Such innovations are set to redefine the role of canned foods in modern diets.
Canned Foods in Specialized Diets

The role of canned foods in various specialized diets is noteworthy. For vegans and vegetarians, canned legumes and vegetables are a convenient and reliable source of essential nutrients. Similarly, many canned foods offer safe, uncontaminated options for those on gluten-free diets. The variety and availability of canned foods make them versatile in diverse dietary practices.
However, individuals with specific dietary needs must be vigilant about ingredients and processing methods. Some canned foods may contain additives or be processed in facilities that handle allergens. Reading labels and choosing products from trusted brands can ensure that canned foods align with one’s dietary requirements.
Consumer Trends in Canned Food Consumption

Consumer trends have seen a shift in the perception and use of canned foods. With growing health and wellness awareness, there is an increasing demand for organic and natural canned products. Consumers are now more inclined to seek out canned foods with fewer additives, lower sodium, and no added sugars.
The fast-paced lifestyle of modern society also influences this trend. The convenience of canned foods, ready to eat or requiring minimal preparation, appeals to those with busy schedules. As a result, manufacturers continually innovate to meet these evolving consumer preferences, offering a wider range of healthier and more convenient options.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, canned foods present a complex array of benefits and drawbacks. While they offer convenience, long shelf life, and accessibility, concerns about nutritional content, health risks, and environmental impact persist. The key lies in informed consumption – understanding the pros and cons, reading labels, and choosing healthier, more sustainable options. As technology and consumer preferences evolve, so will the role of canned foods in our diets, offering a practical yet mindful solution to modern-day food consumption challenges.