The thyroid, an unassuming butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, holds an essential role in your body. It regulates metabolic functions affecting virtually every system in the body. When functioning optimally, the thyroid keeps everything in balance. However, problems arise when the gland is overactive or underactive, leading to a series of thyroid disorders. Understanding these disorders, their causes, and their symptoms is the first step toward a more proactive approach to health.
Contents
Understanding The Thyroid Gland

The thyroid gland is a vital component of the body’s endocrine system, strategically located in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Its primary function is to release hormones that control metabolism—how the body uses energy. The hormones triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) are key players in these processes.
A fascinating aspect of the thyroid gland is its complexity. Despite being small in size, it profoundly affects major bodily functions. It influences the heart rate, body temperature, and even the nervous system. Therefore, any malfunction in the thyroid can have a domino effect on a person’s health, a topic you’ll delve into in the following section.
Common Types Of Thyroid Disorders

Thyroid disorders primarily fall into two categories: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones. Symptoms often include fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, are often culprits behind hypothyroidism, although radiation treatment, certain medications, and thyroid surgery can also be causes.
On the other end of the spectrum is hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by an overproduction of thyroid hormones. This excess can accelerate the body’s metabolism, causing unintentional weight loss, rapid or irregular heartbeat, and irritability. Grave’s disease is the most common cause, but nodules or lumps in the gland can also lead to hyperthyroidism. Additionally, thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer, although less common, are important conditions to be aware of, often presenting as lumps in the thyroid gland.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disorders
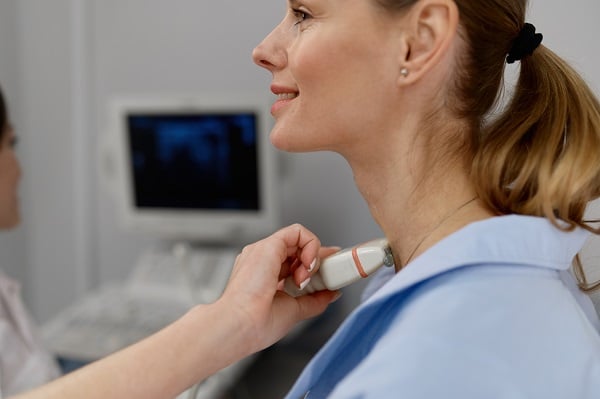
Diagnosing thyroid disorders can be a complex process, as many of their symptoms overlap with other health issues. Medical practitioners often start with a review of the patient’s medical history and a physical exam. Blood tests that measure levels of T3, T4, and TSH hormones provide a more definitive diagnosis.
However, in some cases, further diagnostic procedures may be necessary. Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds or thyroid scans, can provide visual evidence of abnormalities in the thyroid gland, such as nodules or inflammation. A biopsy involving the removal of a small sample of thyroid tissue may also be performed in cases where cancer is suspected. With this arsenal of diagnostic tools, medical professionals can ascertain the nature of a thyroid disorder and devise the most appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment For Hypothyroidism
In cases of hypothyroidism, the most common form of treatment involves daily use of the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine. This oral medication restores adequate hormone levels, reversing the symptoms of hypothyroidism. One should also expect to see improvements in cholesterol levels and, over time, experience a decrease in the size of an enlarged thyroid gland.
It’s important to note that hypothyroid treatment is usually a lifelong commitment, requiring routine blood tests to ensure the dosage is correct. This constant management can seem tedious, but it is crucial to maintain a balance of thyroid hormones in the body. To bolster treatment, certain lifestyle changes and dietary modifications can also prove beneficial in managing this condition.
Managing Thyroid Nodules And Cancer

Thyroid nodules—lumps in the thyroid gland—are often benign and may not require any immediate intervention. In this case, a healthcare provider might suggest a watchful waiting approach. However, if the nodules are large, causing symptoms or suspicious for cancer, surgery might be needed to remove them.
For thyroid cancer, treatments can include surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and external radiation or chemotherapy for advanced cases. The treatment chosen will depend on the type and stage of the cancer and the patient’s overall health. Remember, early detection and treatment often result in better outcomes.
Living With A Thyroid Disorder

Living with a thyroid disorder often necessitates ongoing care and lifestyle adaptations. Adherence to the prescribed medication regimen and routine medical check-ups are crucial to keep the disorder in check. But it’s equally essential to acknowledge the emotional and psychological toll these conditions can take.
Support groups and resources can offer solace and practical advice to individuals grappling with these disorders. A supportive community can provide a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies, fostering resilience in the face of chronic illness. Living with a thyroid disorder may pose unique challenges, but with the right approach, these can be managed effectively.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, thyroid disorders, while common, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the functioning of the thyroid, recognizing the symptoms of common disorders, and exploring the options for diagnosis and treatment can equip individuals to better manage their health. For anyone grappling with a thyroid disorder, remember, you’re not alone. There’s a wealth of support available, from medical professionals to support groups. By actively engaging in your healthcare and tapping into available resources, you can successfully navigate life with a thyroid disorder.