Sugar is everywhere. It’s in the food you eat, drinks, and even the medications you take. And while most people know that sugar isn’t good for them, many don’t understand why. So this article is here to set the record straight! In it, you will learn about sugar’s different effects on your health; it will also provide you with some tips for reducing sugar intake and improving your overall health!
Contents
The Many Uses Of Refined Sugar

Sugar is a versatile ingredient that you can use for everything from making candy to preserving fruit. While it may be most commonly associated with sweetening coffee and baked goods, sugar plays an important role in many aspects of daily life. Sugar is also in the fermentation process of some alcoholic beverages, such as beer and wine. And while people typically think of sugar as being white, there are many different types of sugar, each with its distinct flavor and color.
No matter what form it takes, sugar is a staple in the diets of many people around the world. And while it may be okay in moderation, too much can start to have a negative effect. For example, brown sugar is made by adding molasses to white sugar, while raw sugar is less processed and has a higher level of molasses.
The Effects Of Sugar On Your Health
Too much sugar can harm your health, as hard as it is to avoid. And while it may not seem like a big deal to have a sugary treat every now and then, consuming too much can lead to serious health issues. Here are some of the effects that too much sugar can have on your health:
Weight Gain And Obesity
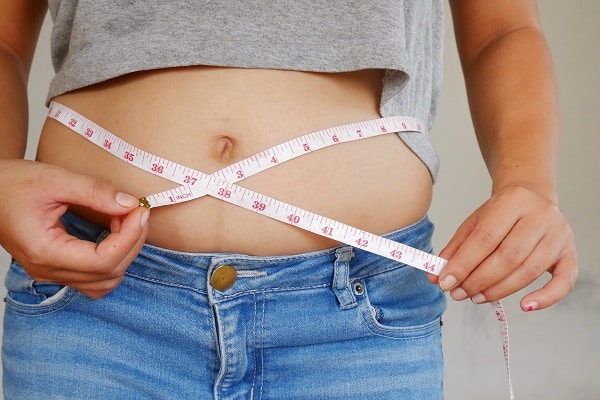

Sugar is often a major cause of weight gain and obesity, but the truth is that it’s only one factor among many. While it’s true that sugar can contribute to an uptick in calorie intake, it’s also important to consider how the body uses those calories. When you consume sugary foods, your body releases insulin to process the sugar. Insulin helps store energy in the form of fat, which can lead to weight gain.
However, not all sugars are created equal. Refined sugars, such as those found in candy and soda, are more likely to cause weight gain than natural sugars, like those found in fruits and vegetables, because refined sugars are absorbed more quickly by the body, causing a spike in insulin levels. So, it’s important to remember to limit your intake of refined sugars and opt for natural sources instead.
Type 2 Diabetes
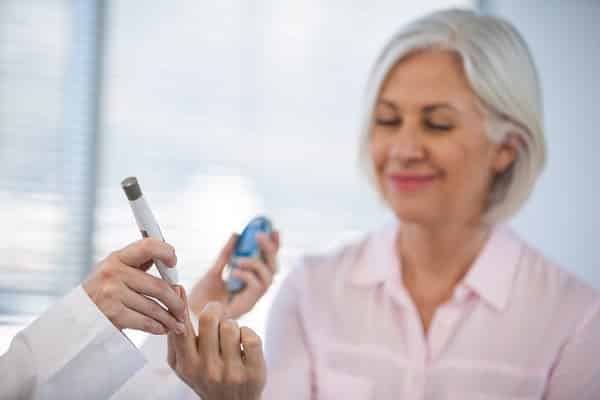

Sugar is a simple carbohydrate in many foods, from fruit to candy to baked goods. When you consume sugar, your body breaks it down into glucose and releases it into your bloodstream. In response, your pancreas produces insulin, which helps to move the glucose into your cells, where it can be used for energy. While it can provide a quick burst of energy, too much sugar can lead to health problems like type 2 diabetes.
But when you consume more sugar than your body can use, the excess glucose builds up in your bloodstream. Over time, this can damage the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas and lead to type 2 diabetes. So while a little sugar may not be harmful, too much can lead to a life-long struggle with diabetes.
Inflammation

While sugar can provide a quick burst of energy, it can also increase inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a response by the immune system to foreign invaders, but factors like stress and obesity can also trigger it. Sugar plays a role in inflammation because it causes an increase in the production of certain cytokines, which are chemicals that promote inflammation. When inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to various health problems, including heart disease and arthritis.
In addition, sugar promotes the release of free radicals, damaging cells and contributing to inflammation. And if you already have a chronic inflammatory condition, consuming too much sugar can worsen symptoms and make it harder to manage the condition.
Heart Disease
For a good reason, sugar is often a dietary villain. Consuming too much sugar can lead to weight gain, increased inflammation, and other health problems. One of the most severe consequences of sugar consumption is heart disease. Sugar intake can cause high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels, which are major risk factors for heart disease.
While sugar is not the only factor contributing to heart disease, it is significant. In addition, sugar promotes the formation of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Thus, reducing sugar intake is essential for maintaining a healthy heart.
Depression

Depression is a severe mental health condition that can profoundly impact every aspect of a person’s life. While the causes of depression are complex and often nuanced, recent research has suggested that sugar may play a role in increasing the risk of this condition. Sugar consumption can cause inflammation, which is a major contributor to depression. In addition, sugar can interfere with the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in regulating mood.
Furthermore, sugar-sweetened beverages have a greater risk of developing depression, particularly among young adults. While more research is needed to confirm these findings, it is clear that sugar can have a significant impact on mental health. Therefore, it is essential to be mindful of sugar intake, especially if you are struggling with depression or another mental health condition.
Tips For Reducing Your Sugar Intake

As you have been learning, too much sugar can lead to many health problems. But reducing your sugar intake doesn’t have to be difficult. Here are a few tips to get you started:
- Cut out sugary drinks. Soda, sports drinks, and even fruit juice are full of sugar. Instead, quench your thirst with water or unsweetened tea or coffee.
- Read nutrition labels. Many processed foods and snacks contain hidden sugars. When you’re grocery shopping, take the time to read the nutrition label and ingredient list to see how much sugar a product contains.
- Stick to whole foods. The best way to reduce your sugar intake is to focus on eating whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. You’ll naturally be less likely to crave sugary snacks and desserts by filling up on nutritious foods.
- Curb your cravings with healthy substitutes. If you have a sweet tooth, satisfy your craving with a healthy alternative like fresh fruit or air-popped popcorn instead of candy or cake. With a little creativity, you can find plenty of delicious ways to cut back on sugar without feeling deprived.
Understand The Effects Of Sugar On Your Health!
Sugar may be a sweet treat, but consuming too much can have serious consequences for your health. By being mindful of your sugar intake and making minor changes to your diet, you can improve your overall well-being and reduce your risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and depression. So think twice before reaching for that sugary snack – your body will thank you in the long run. And if you are struggling to cut back on sugar, consider speaking with a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized guidance and support.


