Understanding the nuanced ways your nocturnal activities influence weight gain is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Many are unaware that certain habits, especially at night, can significantly contribute to unwanted weight. This article sheds light on these common yet often overlooked behaviors, providing insights into why they occur and how they affect our body’s physiology. With each section dedicated to specific nighttime habits, you will gain the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your evening routines, paving the way for healthier choices and better overall well-being.
Contents
Eating Late at Night

Consuming food late at night goes against the natural metabolic processes of the body, which are primed to slow down as you prepare for sleep. Your circadian rhythm dictates not just sleep patterns but also your digestion and metabolism, which are less efficient late at night. Consequently, the body is not as capable of processing food as effectively as it would during the day, leading to potential weight gain. Moreover, the types of foods craved at night are often high in calories and low in nutrients, further exacerbating the problem. Understanding this can be a critical step in adjusting eating schedules for better health outcomes.
The habit of reaching for snacks after dinner can also be attributed to fewer distractions and increased feelings of relaxation, making it easier to give in to cravings. As nighttime approaches, your guard lowers, and you’re more likely to indulge in comfort foods that provide a temporary sense of well-being. Unfortunately, these late-night snacks can lead to a significant increase in total daily calorie intake, contributing to weight gain over time. Recognizing the triggers of late-night eating, such as boredom or stress, can help in developing strategies to combat this weight-inducing habit.
Lack of Sleep

A significant link exists between sleep deprivation and increased appetite, particularly for foods high in fat and sugar. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more ghrelin, a hormone that signals hunger, and less leptin, the hormone that tells you you’re full. This imbalance leads to increased cravings and a tendency to eat more than necessary. Additionally, the fatigue from lack of sleep can reduce physical activity, further contributing to weight gain. Ensuring a full night’s rest is not only beneficial for overall health but also a critical component in maintaining a healthy weight.
Poor sleep doesn’t just affect hormones; it also impairs decision-making and impulse control. Tired individuals are more likely to seek immediate gratification from foods that provide a quick energy boost and emotional comfort. This often results in a preference for unhealthy snacks that are easily accessible and satisfying in the short term. Moreover, the lack of energy from poor sleep can lead to decreased motivation for cooking healthy meals or engaging in exercise, reinforcing the cycle of weight gain. Prioritizing quality sleep is essential for those looking to manage their weight effectively.
Mindless Snacking

Mindless snacking, particularly in the evening, is a common habit contributing to excess calorie intake and weight gain. This often occurs during sedentary activities such as watching TV or scrolling through social media, where attention is diverted, and eating becomes an automatic behavior. The lack of focus on the act of eating leads to a disconnection from hunger cues and satiety signals, resulting in overconsumption. Additionally, the types of foods chosen during mindless snacking are usually high in calories, fats, and sugars, which are detrimental to weight management efforts.
To counteract mindless snacking, it is crucial to develop awareness around food consumption. Implementing strategies such as portioning snacks before starting an activity or choosing healthier alternatives can significantly reduce the impact of this habit. Additionally, engaging in more mindful eating practices, like eating without distractions and savoring each bite, helps promote a better understanding of hunger and fullness. By becoming more attentive to eating habits, individuals can make more informed choices, reducing the likelihood of unnecessary snacking and supporting their weight management goals.
Consuming Caffeine and Alcohol
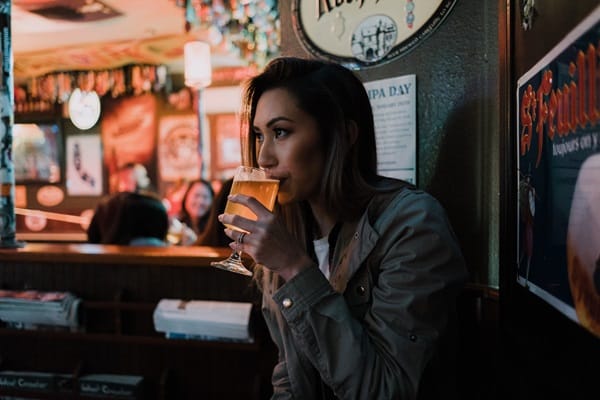

The intake of caffeine and alcohol at night has more implications for weight than many realize. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and some sodas, can significantly disrupt sleep patterns. The lack of quality sleep then contributes to weight gain, as discussed earlier. Alcohol, on the other hand, is not only high in calories but also affects the quality of sleep and decreases metabolism, leading to increased fat storage. The body prioritizes metabolizing alcohol over other nutrients, which means calories from food are more likely to be stored as fat. Understanding these substances’ effects can lead to more mindful consumption, especially in the hours before bedtime.
Moreover, both caffeine and alcohol can alter hunger and fullness hormones, leading individuals to eat more than they might without these influences. Alcohol particularly lowers inhibitions, which can result in overeating or choosing unhealthy foods. To mitigate these effects, limiting the consumption of these beverages in the evening is advisable, opt for caffeine-free alternatives, and understand the potential impact on sleep and eating patterns. Providing the body with a restful environment devoid of stimulants or depressants is a positive step towards maintaining a healthy weight.
Neglecting Hydration
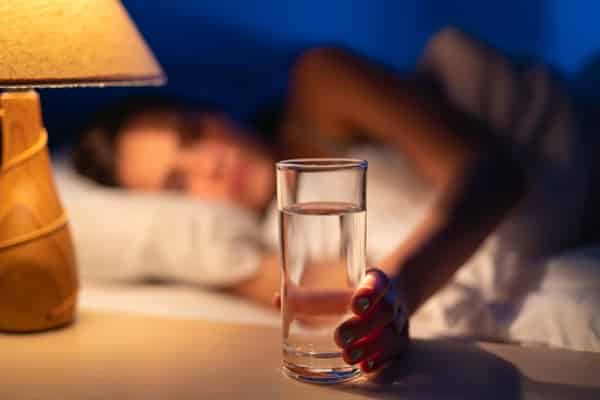

Hydration plays a critical role in weight management, yet its importance is often overshadowed by dietary focus. At night, neglecting to drink enough water can lead to mistaking thirst for hunger, resulting in unnecessary snacking. Proper hydration helps maintain a feeling of fullness, aiding in the reduction of calorie intake. It’s also essential for metabolic processes and helps the body efficiently use the nutrients in the foods consumed throughout the day. Encouraging a habit of regular water intake, particularly in the evening, can significantly impact appetite control and overall calorie consumption.
Dehydration can mimic the sensation of hunger, prompting people to eat when they simply need water. This is especially problematic at night when the body prepares for rest and recovery. Ensuring adequate water intake throughout the day and into the evening can help mitigate this confusion, leading to better hydration and less nighttime snacking. Additionally, choosing water over sugary or alcoholic beverages can substantially decrease the consumption of empty calories. A focus on hydration is not just beneficial for weight but also supports overall health and well-being.
Stress and Emotional Eating
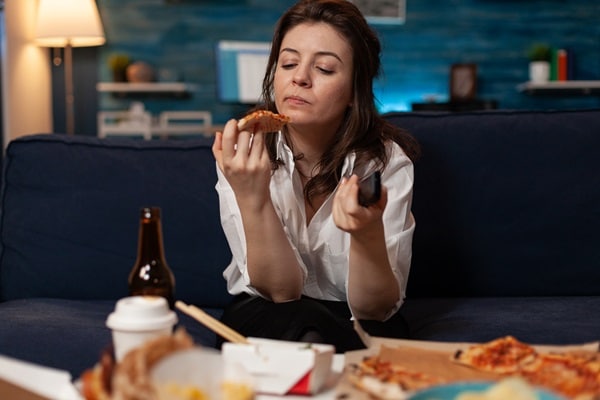

Evening hours can often bring a sense of relief after a long day, yet for many, it’s also a time when stress and emotions peak, leading to emotional eating. This type of eating is rarely about hunger and more about seeking comfort or relief from negative feelings. The foods chosen during emotional eating episodes are often high in calories and low in nutritional value, contributing to weight gain. Recognizing the triggers of stress and emotional eating is a vital step toward addressing this habit. Implementing stress-reduction techniques and finding alternative forms of comfort can significantly reduce the reliance on food for emotional support.
Creating a relaxing evening routine that doesn’t revolve around food is beneficial. Activities like reading, taking a bath, or practicing mindfulness can provide comfort and relaxation without the additional calories. It’s also essential to develop a healthy relationship with food, where it’s seen as nourishment rather than a coping mechanism. By addressing the underlying emotional needs through healthier outlets, the urge to turn to food for comfort can significantly diminish, aiding in weight control and improving emotional well-being.
Inconsistent Eating Schedule
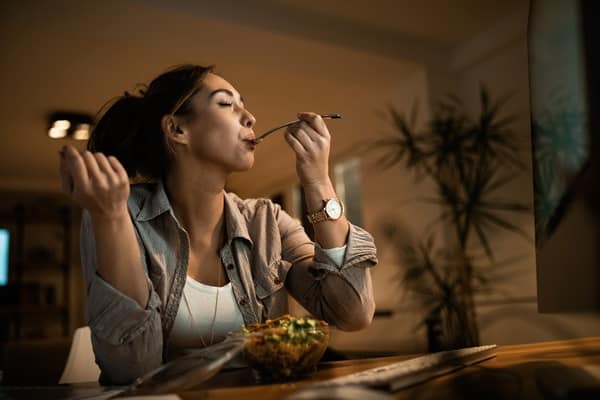

An inconsistent eating schedule can wreak havoc on the body’s internal clock, leading to weight gain and metabolic issues. Eating at irregular times, especially at night, can disrupt the circadian rhythm and negatively impact the metabolism, making it harder for the body to process food efficiently. This can lead to increased fat storage and weight gain. Establishing and maintaining a regular eating schedule aligns with the body’s natural rhythms, supporting better digestion and nutrient absorption. Consistency in meal timing also helps regulate hunger cues, making it easier to avoid unnecessary snacking or overeating.
The variability of an inconsistent eating schedule extends beyond just the timing of meals; it often involves erratic portion sizes and food choices. This unpredictability can make it challenging to maintain a balanced diet and manage calorie intake. By setting regular meal times and sticking to them, individuals can better plan and prepare nutritious meals, reducing the temptation to eat impulsively or choose less healthy options. Regular meal patterns not only support weight management but also contribute to overall health and vitality.
End the Day on a Healthy Note
As you’ve uncovered, nighttime habits play a significant role in weight management and overall health. By addressing these habits, you can make a substantial impact on your weight and well-being. Start tonight by identifying one habit to change and take a step toward a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. Remember, small, consistent changes lead to lasting results. Embrace the journey to better health with each night that passes!